Introduction to Cabergoline
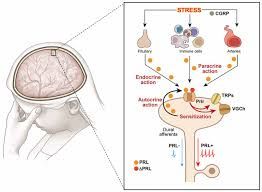
Cabergoline is a potent dopamine receptor agonist that works primarily by reducing the secretion of prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Elevated prolactin levels, known as hyperprolactinemia, can lead to various health issues, particularly affecting reproductive health. Cabergoline is available in various dosages, with Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg being commonly prescribed for managing prolactin levels and treating associated symptoms. By effectively lowering prolactin levels, cabergoline can alleviate a variety of symptoms, restoring hormonal balance, and improving the quality of life.
What causes high prolactin levels?
Hyperprolactinemia can arise from several underlying causes, including:
-
Pituitary Tumors: Prolactinomas, benign tumors in the pituitary gland, can lead to excess prolactin production. These tumors are often responsible for the majority of hyperprolactinemia cases.
-
Medication: Certain drugs, including antipsychotics, antidepressants, and anti-nausea medications, may increase prolactin levels.
-
Stress: Emotional and physical stress can trigger short-term rises in prolactin, although these are usually temporary.
-
Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid function can result in elevated prolactin levels as the body attempts to compensate for low thyroid hormone production.
-
Chronic illness: liver or kidney disease may impair the clearance of prolactin from the bloodstream, leading to higher levels.
Understanding these potential causes can aid in diagnosing and treating hyperprolactinemia effectively. Cabergoline’s mechanism of action makes it a preferred choice for managing prolactin levels in cases resulting from pituitary tumors, medication-induced increases, or other treatable causes.
Mechanism of Action of Cabergoline
Cabergoline works by binding to dopamine D2 receptors in the pituitary gland. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, inhibits prolactin release under normal conditions. By mimicking dopamine’s effects, caffeine stimulates dopamine receptors, reducing prolactin secretion. This mechanism helps balance hormone levels, preventing or alleviating hyperprolactinemia symptoms.
Benefits of Cabergoline Treatment
-
Restores reproductive health: high prolactin levels disrupt the production of sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone, affecting menstrual cycles and sperm production. Cabergoline treatment can help restore normal menstrual cycles in women and boost fertility in men.
-
Improves Sexual Function: Reduced prolactin levels positively impact sexual health, enhancing libido, arousal, and performance.
-
Reduces Physical Symptoms: Hyperprolactinemia often causes symptoms like breast tenderness, gynecomastia (breast enlargement in men), and galactorrhea (milk discharge from breasts in non-lactating individuals). Cabergoline can alleviate these discomforts by lowering prolactin levels.
-
Protects Bone Health: Chronically elevated prolactin can lead to low estrogen or testosterone levels, weakening bones and increasing fracture risk. Cabergoline’s ability to normalize hormone levels helps maintain bone density and reduce osteoporosis risk.
-
Improves Mental Health: High prolactin levels may contribute to depression, mood swings, and fatigue. By balancing hormones, caffeine helps improve overall mental well-being.
Dosage Guidelines for Cabergoline
Cabergoline is typically prescribed in doses of 0.5 mg or 0.25 mg, depending on the severity of hyperprolactinemia and individual tolerance. Treatment should always be guided by a healthcare professional, as the exact dosage and frequency can vary.
-
Starting Dosage: A common starting dose is 0.25 mg taken twice a week, gradually adjusted based on response and tolerance.
-
Adjustment Phase: If prolactin levels remain high, the dose may be increased in increments of 0.25 mg after several weeks. It’s important to monitor for any adverse reactions during this phase.
-
Maintenance Dose: The goal is to maintain prolactin at normal levels with the lowest effective dose, often between 0.5 mg and 1 mg weekly in divided doses.
-
Duration of Treatment: Cabergoline treatment may last several months or even years, depending on the underlying cause. Regular blood tests help track prolactin levels and assess the treatment’s efficacy.
Possible Side Effects of Cabergoline
Like any medication, cabergoline may cause side effects. Being aware of these helps users anticipate potential reactions and consult their healthcare provider when necessary.
-
Common Side Effects:
- Nausea: Cabergoline can cause nausea, especially in the early stages. Taking it with food or at night may help.
- Headaches: Headaches may occur as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Dizziness: Dizziness, especially upon standing, is a known side effect due to cabergoline’s effect on blood pressure.
- Fatigue: Some users report mild to moderate fatigue when starting treatment.
-
Serious Side Effects (rare):
- Heart Valve Issues: Although rare, high doses or prolonged use of cabergoline have been linked to an increased risk of ventricular heart disease.
- Psychiatric Effects: Hallucinations, mood swings, or compulsive behaviors have been observed, although infrequent.
- Severe Nausea or Vomiting: Persistent gastrointestinal symptoms should be addressed with a healthcare provider.
Cabergoline’s Role in Treating Prolactinoma
Cabergoline is highly effective in treating prolactinoma, a type of pituitary tumor that causes excess prolactin. Research shows that cabergoline not only reduces prolactin levels but can also shrink prolactinoma size. Many individuals with prolactinomas achieve normal prolactin levels within a few months of treatment, often without surgery. This non-invasive option makes cabergoline a preferred first-line treatment for prolactinoma.
-
Effectiveness: Studies report that cabergoline effectively reduces prolactinoma size in up to 90% of patients, making it an optimal choice for individuals with prolactin-secreting tumors.
-
Monitoring: Regular MRI scans and blood tests allow for close monitoring of prolactinoma size and prolactin levels, ensuring the treatment is on track.
-
Avoidance of Surgery: By reducing tumor size, cabergoline minimizes the need for surgical intervention, which can carry its own risks and complications.
Cabergoline for Treating Other Conditions
Besides hyperprolactinemia, cabergoline has shown promise in managing other medical conditions:
-
Parkinson’s Disease: Due to its dopamine agonist action, cabergoline can alleviate some symptoms of Parkinson’s, such as motor fluctuations, stiffness, and tremors. However, it is typically used in combination with other medications and under close medical supervision.
-
Cushing’s Disease: Some individuals with Cushing’s disease, a condition marked by high cortisol levels, benefit from cabergoline. Although less common, cabergoline may reduce cortisol secretion by affecting the pituitary gland.
-
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Cabergoline has been explored as a treatment for RLS due to its dopamine-modulating effects. However, other medications are typically preferred due to side effects associated with long-term cabergoline use.
Comparing Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg
While both dosages (0.5 mg and 0.25 mg) are effective, choosing the right dose depends on individual needs, tolerance, and response.
-
Cabergoline 0.5 mg:
- Often prescribed to individuals with significantly elevated prolactin levels.
- Tends to have a stronger effect but may increase the likelihood of side effects.
- Typically administered once or twice a week.
-
Cabergoline 0.25 mg:
- Commonly used as a starting dose to gauge response and limit side effects.
- Ideal for individuals with mild to moderate prolactin elevation.
- Dosage can be adjusted based on prolactin levels and patient tolerance.
-
Individualized Approach: A healthcare provider will determine the best dose based on prolactin levels, patient health, and symptom severity. Starting with a lower dose like 0.25 mg and adjusting gradually helps minimize adverse effects.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
While on cabergoline treatment, lifestyle modifications can help improve overall health and hormone balance.
-
Balanced Diet: A nutrient-rich diet supports hormone balance and overall health. Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D are beneficial for bone health, countering potential bone loss due to high prolactin levels.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps reduce stress and can alleviate some of the mood-related symptoms associated with hormonal imbalance.
-
Avoidance of Alcohol and Smoking: Alcohol and smoking may impact cabergoline’s effectiveness and exacerbate side effects, so limiting these substances is advisable.
-
Routine Monitoring: Regular blood tests are essential for monitoring prolactin levels, adjusting cabergoline dosage, and preventing complications.
Conclusion
Cabergoline, available in 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg doses, is a highly effective treatment for managing hyperprolactinemia and its symptoms. Through its dopamine-agonist action, cabergoline reduces prolactin secretion, restoring hormonal balance and alleviating symptoms. From managing prolactinoma to improving reproductive health, mental well-being, and bone density, caffeine offers numerous benefits.
Careful monitoring, proper dosage adjustment, and regular follow-ups are essential to ensuring the best outcomes. Lifestyle modifications further enhance treatment efficacy, supporting overall health. Cabergoline remains a valuable treatment option in endocrinology, offering relief to those affected by high prolactin levels and contributing to better quality of life.